Autism Spectrum Condition (ASC)
Autism Spectrum Condition (ASC) is characterised by challenges with social communication and interaction, as well as restricted and repetitive patterns of behaviour, interests or activities. ASC is often diagnosed in early childhood, but some individuals may not receive a diagnosis until later in life.
ASC is a spectrum neurodifference, meaning that traits can range from mild to severe, and as with all neurodifferences, it can impact all individuals differently. Many autistic individuals may possess unique skills such as strong attention to detail, analytical skills, good memory and pattern recognition, as well as having in-depth knowledge on specific subjects.
However, individuals may find challenges with some everyday tasks, such as interpreting the behaviour and intentions of other people or maintaining eye contact during a conversation.
Research into ASC has increased in recent years, leading to a better understanding of the neurodifference and improved support for autistic individuals and their families. Despite this progress, there is still much to learn about ASC, and ongoing research is necessary to improve our understanding of the neurodifference and develop effective methods of support.
What is ASC?
Autism Spectrum Condition (ASC) is a neurodifference that affects an individual's social interaction, communication, and behaviour. It is a spectrum condition because it affects individuals in different ways and to varying degrees.
Autistic individuals may have challenges understanding social cues, such as body language and facial expressions, and communicating effectively with others. They may also engage in repetitive behaviours or have more narrow interests.
ASC is a lifelong neurodifference that is typically diagnosed in early childhood, although some individuals may not receive a diagnosis until later in life. It is estimated that around 1 in 100 people in the UK are autistic. Whilst more males are diagnosed with autism than females, the number of females being diagnosed is steadily growing as awareness of autistic traits amongst girls and women increases.
With the right support, autistic individuals can thrive in education and work, maximising their strengths and developing strategies to address challenges they may experience.
It is important to note that ASC is not caused by poor parenting or environmental factors, and autistic individuals should not be stigmatised or discriminated against. With understanding and support, autistic individuals can lead happy and successful lives.
Signs of ASC may Include:
Challenges interpreting the behaviour and intentions of other people
Intense interests
A tendency for compulsive or repetitive behaviours
Finding relationships challenging
Finding changes to routines challenging
Having trouble describing emotions
Having challenges with back and forth conversation
“The first few weeks in my new job were overwhelming. I don’t like surrounding myself with too many people, and there were a lot of rules to get used to. But then I got a workplace mentor who explained some of the rules about using the work kitchen, and they helped me to draw up a timetable of my working day so everything was in small chunks of time.”
- Katherine,
Junior Finance Associate
Common Strengths Associated with ASC
Autistic individuals often possess unique strengths and talents which can be utilised to great effect in a variety of settings.
One of the most notable strengths of autistic individuals is an ability to focus intensely on a particular task or topic. This ability, known as hyperfocus, enables many autistic individuals to become experts in their chosen field, and to produce work of a consistently high standard.
Another skill commonly found in autistic individuals is attention to detail. This skill enables them to spot errors and inconsistencies that might often be missed by others, and to produce work that is most often accurate and precise.
Autistic individuals may also possess exceptional memory skills. This can include both short-term memory, allowing them to recall information quickly and accurately, and long-term memory, allowing them to retain vast amounts of information over extended periods of time.
Autistic individuals often have a unique perspective on the world, which can provide valuable insights and ideas. This perspective can be particularly useful in creative fields, where new and innovative ideas are highly prized.
These unique strengths can make autistic individuals highly valuable contributors to a wide range of industries and settings. By recognising and utilising such skills, we can create a more inclusive and diverse society that benefits everyone.
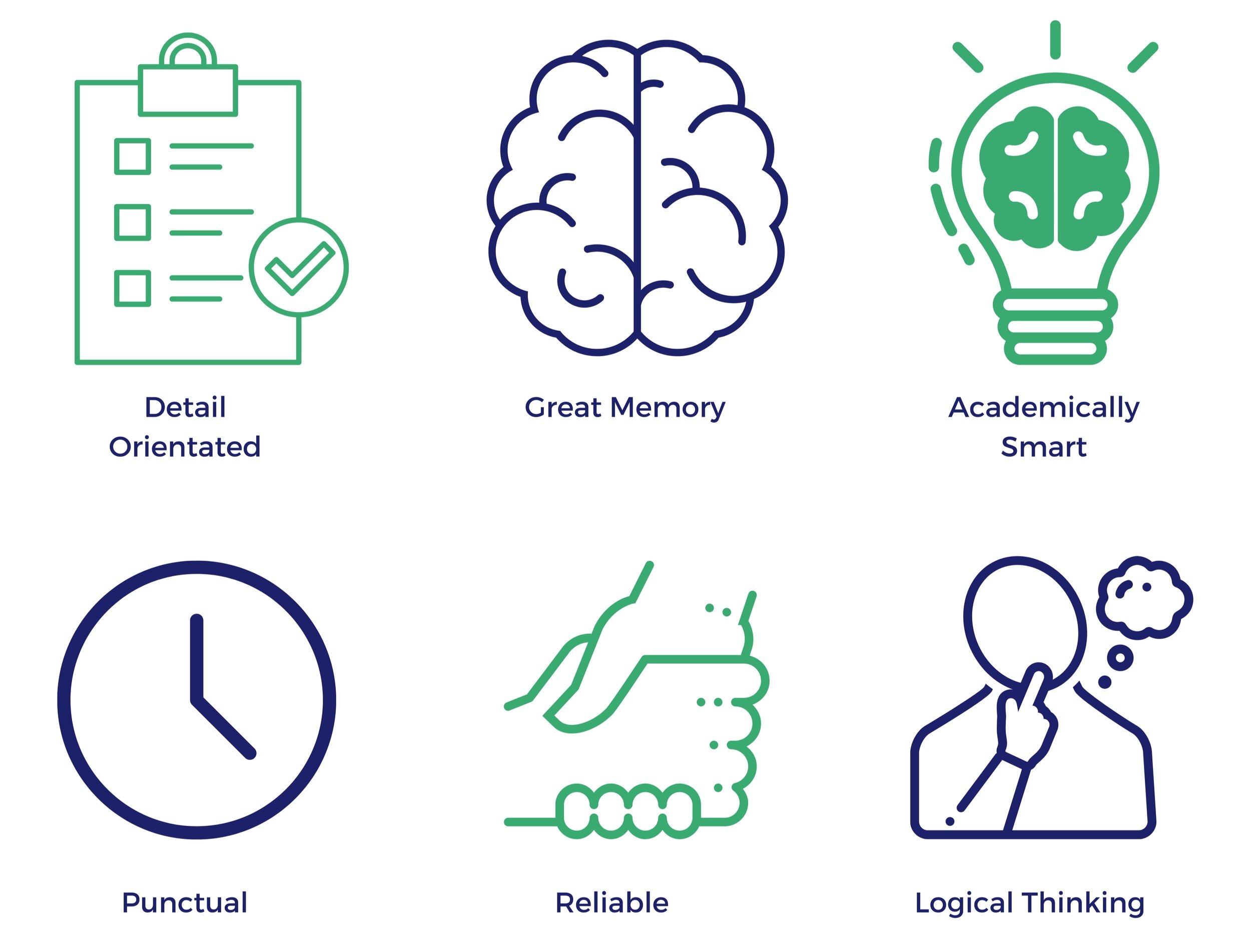
Many autistic individuals possess unique skills. These skills vary from person to person, but commonly include logical thinking, reliability, great memory and being very detail orientated.
Common Traits of Autism Spectrum Condition
-
Autistic individuals may have repetitive behaviours and routines, such as lining up objects or repeating certain phrases. They may also have intense interests in specific topics and may find it challenging if their routines or interests are disrupted. Autistic individuals may also have challenges with social interactions, such as making eye contact, understanding nonverbal cues, and initiating conversations.
-
Communication challenges are a hallmark of ASC. Some autistic individuals may have delayed speech or language development, and they may have challenges with understanding and using language effectively. They may also have challenges with social communication, such as taking turns in conversation or understanding sarcasm and humour. However, the honesty and direct communication style possessed by many autistic individuals can be very useful in the workplace.
-
While ASC is primarily related to the brain, there may be physical traits associated with the neurodifference. For example, autistic individuals may have sensory processing challenges, such as being oversensitive or undersensitive to certain sounds, light, textures, or tastes. They may also have fine motor challenges, such as challenges with handwriting or manipulating small objects.
It's important to note that not all autistic individuals will exhibit these traits, and some may exhibit additional traits not listed here.
Did You Know?
Some autistic individuals aren’t diagnosed until adulthood
Three times as many men as women are diagnosed with ASC
Every autistic person is unique
Many famous people have ASC
(for example, Wentworth Miller, Hannah Gadsby and Courtney Love)
Diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Condition
The diagnosis of ASC involves a comprehensive assessment that includes a detailed medical and developmental history, behavioural observations, and standardised assessments of social communication, language, and cognitive abilities. The assessment may also include medical evaluations to rule out other neurodifferences that may present with similar symptoms.
Early diagnosis of autism can significantly enhance outcomes for individuals with Autism Spectrum Condition (ASC).
Typically, the diagnostic process is led by one or more clinicians, such as a psychologist and a speech and language therapist, however the process may also include specialists like psychiatrists, occupational therapists, or paediatricians, depending on the individual’s age. These professionals collect evidence during the assessment and consult a multi-disciplinary team to reach conclusions regarding the assessment. The team will collaborate to assess the individual's strengths and challenges and to create a personalised support plan that addresses their specific needs.
The diagnosis of ASC is based on a set of criteria specified in the DSM-5 and ICD-11. It is important to note that while the official diagnostic criteria uses the term Autism Spectrum Disorder, we prefer to use the more positive term Autism Spectrum Condition.
Living with Autism Spectrum Condition
Daily Life
Daily life can be overwhelming for many autistic individuals due to sensory sensitivities and challenges with social communication. Whilst every autistic individual is different, it can be helpful to create a structured routine and environment to help manage these common challenges. This may include:
Using visual schedules and reminders to help with time management and transitions
Creating a sensory-friendly environment by reducing noise and lighting
Practicing social skills and communication through role-play and social stories
Finding activities that match individual interests and strengths
It is also important to have a support network of family, friends, and professionals to provide guidance and assistance when needed.
At Work
Finding and maintaining employment can sometimes be a challenge for autistic individuals, but it is important to recognise that with the right accommodations and support, many autistic individuals will excel in their roles at work.
"Employees on the autism spectrum were as much as 140 percent more productive than their peers."
- James Mahoney, Executive Director and head of Autism at Work for JPMorgan Chase
Whilst it is important that employers listen to the individual to find out what support and accommodations work for them, some common adjustments or accommodations can include:
Flexible work hours or schedule
Sensory-friendly work environments
Communication support, such as written instructions or visual aids
Advance notice and explanation of changes.
Autistic individuals may also benefit from vocational training and support to develop job skills and find suitable employment opportunities.
Living with ASC may present unique challenges, but with understanding and support, autistic individuals can lead fulfilling lives and contribute to society in many valuable ways.
Download our ASC Information Sheet:
This information sheet has been created by our team of expert psychologists, and provides information about ASC, common challenges, and suggestions of the support available.
How Can Lexxic Help?
At Lexxic, we have a range of diagnostic tools to help assess your needs, or the needs of your employees.
Our team of highly qualified psychologists provide support and advice for adults in the workplace. We work with you from the point of diagnosis, through to identifying what you need to get the best long-term outcomes.
We can help you to better understand your strengths and challenges, know your learning style, and give you training for specific skills.
Get in touch if you would like to chat with one of our team, or find out more about the services we can provide.